Puppy Fitness That Fits The Puppy Age Appropriate Exercise Guidelines
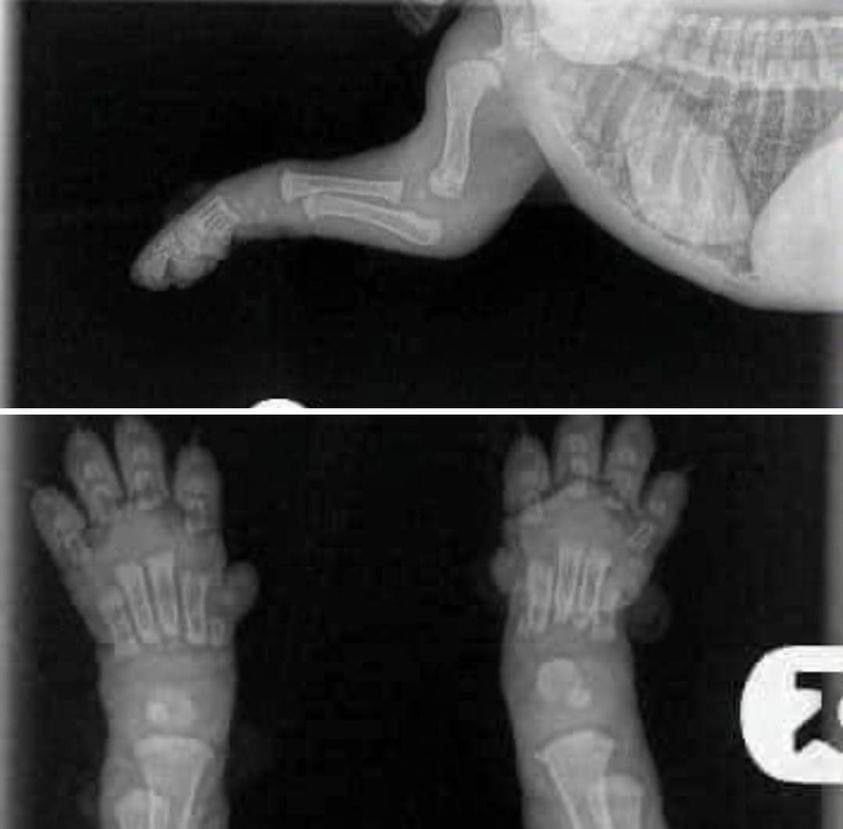
No Bones About It... Puppies Aren’t Miniature Dogs
The first consideration with puppy exercise is something called “growth plates.” Growth plates are soft areas that sit at the ends of the long bones in puppies and young dogs. They contain rapidly dividing cells that allow bones to become longer until the end of puberty. Growth plates gradually thin as hormonal changes approaching puberty signal the growth plates to close. In puppies, this closure is normally completed by approximately 18 months old.
Until the growth plates close, they’re soft and vulnerable to injury. After sexual maturity, the growth plates calcify and the rapid cell division ends. The growth plate becomes a stable, inactive, part of the bone, now known as an epiphyseal line.
A dog’s bones are held together with muscles, tendons, and ligaments - soft tissue. In an adult dog, if a joint experiences a stress such as bending the wrong way or rotating too much, the bones will hold firm and a soft tissue will be pulled, resulting in a sprain. In a puppy, however, his muscles, ligaments and tendons are stronger than his growth plates, so instead of a simple sprain, his growth plate is liable to be injured - the puppy’s own soft tissue can pull apart his growth plate.
Why this matters so much is that, unlike a sprain, injuries to the growth plate may not heal properly or not heal in time for the puppy to grow up straight and strong. Injury to a growth plate can result in a misshapen or shortened limb which, in turn, can create an incorrect angle to a joint which can make the puppy more prone to yet more injuries when he grows up.
Puppies Are Soft Core
In addition to having soft growth plates at the end of long bones, a puppy’s bones in general are “softer.” Dogs, like people, don’t reach their maximum bone density until after puberty.
Spiral fractures of the tibia (lower leg bone) are very common in puppies - 50% of all fractures occur in puppies under 1 year of age. A spiral fracture is where the bottom half of the bone twists in one direction and the top half twists in the other.This kind of juvenile injury is known as “Toddler Fracture” in humans, and it’s thought to be caused by the fact that the outside, fibrous layer of the bone (periosteum) is relatively strong in relation to the elastic bone inside. So any exercise that puts torque on (twists) a bone puts the puppy at risk for a fracture.
Puppies Are In It For The Short Run
Puppies naturally exercise in small bursts of activity, not sustained walks. Puppies don’t have the cardiovascular system for endurance. Furthermore, until they mature, they're probably not able build much endurance no matter how much they exercise.
In human children, sustained exercise only increases aerobic capacity by up to 10%. In adults, that kind of exercise can increase aerobic capacity by up to 30%. Long walks and exercise sessions increase risk of injury and yield few benefits for puppies, so endurance training is better left until the puppies have grown up.
Bubble Puppies Don’t Build Bone
After reading about growth plates and toddler fractures, you may find yourself clutching your puppy, afraid to let him move lest he breaks a limb. Relax! Not only is appropriate exercise not dangerous for your puppy, exercise has been shown to increase bone density in children.
Furthermore, those children who exercised were a whopping 50% less likely to fracture a bone. There’s every reason to believe the same holds true for dogs, so appropriate exercise is key to building strong bones in your puppy and preventing adult fractures. So let’s talk about guidelines for puppy exercise. Exploring low rock walls and gardens at their own pace is great mental and physical exercise for puppies.
Self Directed Play is an overriding rule for any puppy under 18 months old. The majority of his exercise should be free play, exploring, and noodling around. If he shows any fatigue, flops down, refuses to walk, you should listen to him and let him rest.
Repetition Is Your Enemy
Probably the biggest cause of growth plate and soft tissue injury is repetitive exercise with a young puppy. So, until he’s about 18 months old, long hikes and walks are out and lots of free-play sessions are in.
Sniff 'N Stroll
While long hikes are out, just tooling around in the backyard with you is great. If you don’t have a backyard, short, rambling walks are perfect. Let your puppy sniff, explore and take it at his own pace. You can intersperse short training sessions in your walks to work on heeling/loose leash walking, but the majority of the walk should be at your puppy’s own pace and at his discretion.
Speaking of hikes, if you’re an outdoorsy type of person, you should bring your puppy along on hikes - it's great socialization for puppies under 12 weeks old, and great enrichment for older puppies. But just like when you take a small child on a walk, be prepared to carry your puppy a good portion of the way. If you’re jogging or walking on a manicured trail or paved park road, consider investing in a puppy stroller to put your tyke in for most of the walk.
Be A Puppy Matchmaker
A gentle giant may be a better playmate than a over-the-top small dog. Play with a well-matched and gentle playmate is ideal. Size is a factor, as a very large dog, especially one that likes to play with a lot of paw whacks, can inadvertently injure a young or small breed puppy.
That being said, a gentle Wolf Hound may be a better playmate than a feisty Jack Russell Terrier who likes to body slam. Keep a very careful eye out and be prepared to throw handfuls of cookies down to interrupt any overly physical play. Body slams and crazy rolls are spiral fractures waiting to happen!
Soft Landings
Jumping off of beds and couches are major causes of spiral fractures in puppies - we are constantly on guard until our puppies reach two years old and keep them off furniture and beds unless we’re there to help them off. We also use heavy carpet pads and carpets around all furniture and beds to cushion impact, should a young (or old) dog slip by and get up on a high piece of furniture.
You can start training in agility but no jumping higher than wrist height until 6 months old, no jumping higher than elbow height until 18 months old.
Stairs Aren't Hip
A study of 500 Newfoundland, Labrador, and Leonberger puppies found that puppies who climbed flights of stairs daily before they were 3 months of age had an increased risk of developing hip dysplasia. Although these breeds were selected for the study because of their relatively high incidence of hip dysplasia, the study seems to indicate that stairs represent a strain on any puppy’s joints, so consider ramps or carrying your puppy down stairs if possible.
Play Nice
Puppies often have more “will” than “way” when it come to chasing toys and will not stop until they are literally on top of the toy, causing both heavy impact and twisting on the bones and soft tissue. We advise rolling balls or dragging toys on the ground for all puppies. Tug toys should be held low and steady - don’t pull up or back on your puppy’s neck!


